Industry-news
What Is A Laser Cutting Machine?
What is a laser cutting machine?
Laser cutting machine is a CNC device that uses high-energy laser beams to accurately cut or engrave materials. Its core principle is to melt and gasify the material instantly by focusing the high temperature generated by the laser beam, and blow away the melt with auxiliary gas to achieve efficient and high-precision cutting effect.
The following is a specific analysis:

1. Core components
Laser generator
Generates a high-power density laser beam. Common types include CO₂ lasers, fiber lasers, etc.
Optical path system
Contains reflectors, focusing lenses, etc., which are used to guide and focus the laser beam to the surface of the workpiece.
CNC system and motion mechanism
CNC device: Controls cutting paths and parameters through programming to support complex graphics processing.
Beams and guide rails: Such as gantry beam design, equipped with reinforcing rib structure to improve stability.
Auxiliary system
Includes cooling devices (such as chillers), gas injection systems (blowing away slag), etc.
2. Working Principle
Energy Focusing
The laser beam is focused into a tiny spot (about 0.1mm in diameter) by the optical path system, and the energy density can reach 10⁶~10⁷ W/cm², instantly heating the material to the melting point or boiling point.
Material Removal
High-pressure gas (such as oxygen, nitrogen) is coaxially sprayed with the laser to blow away the molten or vaporized material to form a cutting seam.
Dynamic Cutting
The relative movement of the laser head and the workpiece is controlled by the CNC system to achieve a continuous cutting trajectory67.
3. Core Advantages
High Precision: The incision width is only 0.1~0.3mm, and the repeat positioning accuracy can reach ±0.05mm38.
High Efficiency: The cutting speed far exceeds that of traditional mechanical tools, suitable for mass production.
Flexibility: Supports cutting of any plane graphics, no mold is required, and saves materials.
Low Damage: Non-contact processing to avoid scratches or deformation of the workpiece surface. IV. Application scenarios
Industrial manufacturing
It is used for cutting metal sheets (such as stainless steel, aluminum alloy) and non-metals (acrylic, wood), and is widely used in the fields of automobiles, aerospace, etc.
Creative processing
Complex pattern engraving, artwork production, etc.
Precision electronics
Fine cutting of microelectronic components and circuit boards.
V. Operation specifications
Safety protection
Wear special protective glasses to avoid looking directly at the laser beam or cutting sparks.
Equipment inspection
Confirm that the cooling system (such as chiller) is operating normally and the laser is stable before starting.
Parameter matching
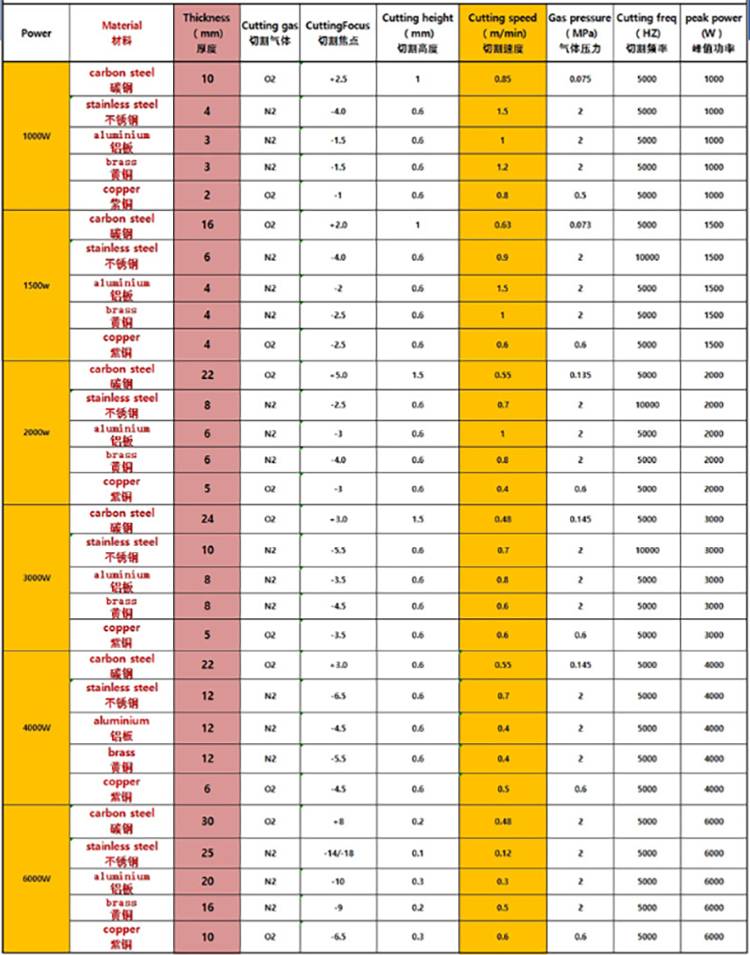
Adjust laser power, gas pressure and other parameters according to material type and thickness.
Process monitoring
It is forbidden to leave the post during processing, and the machine will be shut down for maintenance immediately if abnormalities are found.





Laser cutting machines have become key equipment for improving processing efficiency and precision in modern manufacturing by integrating optical, mechanical and CNC technologies.